Kubernetes deployment
This is the continuation of the Getting Started With Grains tutorial. For now, the tutorial showed how to run multiple members locally using Consul. The same setup might be also suitable for some deployment cases, but since modern applications are more often deployed in Kubernetes, it is better to select dedicated provider for it.
Kubernetes provider is another implementation of IClusterProvider interface, the same as
Consul provider. For more information you can check
Cluster providers section.
MANDATORY READING!!
The essential configuration is CPU Requests combined with No CPU Limits. Deviating from this configuration results in CPU throttling, leading to gossip timeouts and associated issues.
This is not an issue specific to Proto.Actor; rather, it is a problem inherent to real-time systems within Kubernetes. Real-time systems cannot tolerate intermittent CPU pauses on nodes, as this unpredictably renders them unresponsive for undefined durations.
Changes in the application
First thing that needs to be done is to reference Proto.Cluster.Kubernetes package where this implementation is provided.
The next step is to replace Consul provider with Kubernetes provider in ActorSystemConfiguration.cs.
...
var clusterConfig = ClusterConfig
.Setup(
clusterName: "ProtoClusterTutorial",
clusterProvider: new KubernetesProvider(),
identityLookup: new PartitionIdentityLookup()
)
It is also needed to change how remote configuration is prepared. We bind to all interfaces and use ProtoActor:AdvertisedHost host address passed in the configuration.
var remoteConfig = GrpcNetRemoteConfig
.BindToAllInterfaces(advertisedHost: configuration["ProtoActor:AdvertisedHost"])
.WithProtoMessages(MessagesReflection.Descriptor);
To have configuration variable in AddActorSystem extension it is needed to change its signature.
public static void AddActorSystem(this IServiceCollection serviceCollection, IConfiguration configuration)
{
...
}
And usage in ProtoClusterTutorial Program.cs.
builder.Services.AddActorSystem(builder.Configuration);
The same in the SmartBulbSimulatorApp
services.AddActorSystem(hostContext.Configuration);
At this step both applications should be ready to run in Kubernetes, but first we need to create conainter images.
Create docker images
To continue next steps it is needed to have container registry where the images will be pushed. In our tutorial we will use Azure Container Registry. You can find instructions how to create it here.
Add Dockerfile into ProtoClusterTutorial directory:
# Stage 1 - Build
FROM mcr.microsoft.com/dotnet/sdk:6.0 AS builder
WORKDIR /app/src
# Restore
COPY *.csproj .
RUN dotnet restore -r linux-x64
# Build
COPY . .
RUN dotnet publish -c Release -o /app/publish -r linux-x64 --no-self-contained --no-restore
# Stage 2 - Publish
FROM mcr.microsoft.com/dotnet/aspnet:6.0
WORKDIR /app
RUN addgroup --system --gid 101 app \
&& adduser --system --ingroup app --uid 101 app
COPY --from=builder --chown=app:app /app/publish .
USER app
ENTRYPOINT ["./ProtoClusterTutorial"]
After this you should be able to build docker image for the ProtoClusterTutorial app with tag:
docker build . -t YOUR_ACR_ADDRESS/proto-cluster-tutorial:1.0.0
You need to add Dockerfile in the SmartBulbSimulatorApp directory too:
# Stage 1 - Build
FROM mcr.microsoft.com/dotnet/sdk:6.0 AS builder
WORKDIR /app/src
# Restore
COPY /ProtoClusterTutorial/*.csproj ./ProtoClusterTutorial/
COPY /SmartBulbSimulatorApp/*.csproj ./SmartBulbSimulatorApp/
RUN dotnet restore ./SmartBulbSimulatorApp/SmartBulbSimulatorApp.csproj -r linux-x64
# Build
COPY . .
RUN dotnet publish ./SmartBulbSimulatorApp/SmartBulbSimulatorApp.csproj -c Release -o /app/publish -r linux-x64 --no-self-contained --no-restore
# Stage 2 - Publish
FROM mcr.microsoft.com/dotnet/aspnet:6.0
WORKDIR /app
RUN addgroup --system --gid 101 app \
&& adduser --system --ingroup app --uid 101 app
COPY --from=builder --chown=app:app /app/publish .
USER app
ENTRYPOINT ["./SmartBulbSimulatorApp"]
SmartBulbSimulatorApp relies on ProtoClusterTutorial sources so you need to run it from the main directory and pass Dockerfile as argument.
docker build -f SmartBulbSimulatorApp/Dockerfile . -t YOUR_ACR_ADDRESS/smart-bulb-simulator:1.0.0
So now we created images for both applications and they should be visible on the images list:
docker images
Tip: If you encounter strange errors during building images then remove obj and bin directories. You can also consider adding .dockerignore file to skip them.
Both images should be pushed to our container registry:
docker push YOUR_ACR_ADDRESS/proto-cluster-tutorial:1.0.0
...
docker push YOUR_ACR_ADDRESS/smart-bulb-simulator:1.0.0
Now both images are stored in the container registry and we can start application deployment.
Deployment to Kubernetes cluster
To continue next steps it is needed to have Kubernetes cluster running. In our tutorial we will use Azure Kubernetes Service. You can find instructions how to create it here.
To simplify the deployment to Kubernetes we will use
Helm. Ensure that you have installed it locally and helm command is available. You can check how to do it
here
Now we are going to prepare Helm chart that will help us with deployment.
To not create everything by hand you can download chart-tutorial
folder from tutorial’s repository on Github.
This chart contains definitions of following resources:
- deployment - the most important part is setting
ProtoActor__AdvertisedHostvariable based on pod’s IP
env:
- name: ProtoActor__AdvertisedHost
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
fieldPath: status.podIP
-
service - to make each member reachable by another members
-
role - permissions needed for Kubernetes cluster provider
-
service account - identity in Kubernetes that will be used by pod (Kubernetes provider)
-
role binding - connection between role and service account
To continue with deployment you should open values.yaml and replace member.image.repository with your image. The same with member.image.tag. Key member.replicaCount determines the number of running replicas. By default it it 2.
After this, you need to open terminal in a chart’s folder parent directory. Then you need to run helm install to deploy your image.
helm install proto-cluster-tutorial chart-tutorial
Where proto-cluster-tutorial is the name of the release and chart-tutorial is the name of a folder where the chart is located.
After this you should be able to see in the command line information that deployment is succeeded.
helm install proto-cluster-tutorial chart
You can also check that there are two running pods:
$ kubectl get pods
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
proto-cluster-tutorial-886c9b657-5hgxh 1/1 Running 0 63m
proto-cluster-tutorial-886c9b657-vj8nj 1/1 Running 0 63m
If we will look closer to the created pods, we can see labels that were added by Kubernetes provider here.
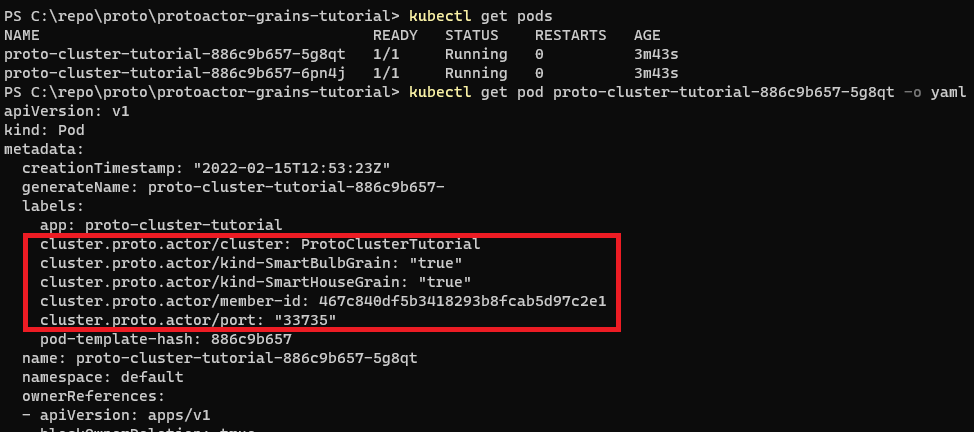
At this point these pods do nothing. Now it is needed to deploy simulator. We can reuse the same chart because simulator uses cluster client to send data to proto.actor cluster and requires similar permissions.
To do this we will call helm install as before but we will override values saved in values.yaml file. So first let’s copy values.yaml file and rename it to simulator-values.yaml.
In the file we will change repository and tag to align with simulator image pushed to container registry. We also change replicaCount to 1 because we would like to have only single replica of the simulator.
Then we open again terminal in chart’s parent directory and deploy simulator. We are adding --values parameter override values.yaml stored in chart’s folder.
helm install simulator chart-tutorial --values .\simulator-values.yaml
We can also see that the pod has been deployed and we can see one more pod:
$ kubectl get pods
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
proto-cluster-tutorial-886c9b657-5hgxh 1/1 Running 0 98m
proto-cluster-tutorial-886c9b657-vj8nj 1/1 Running 0 97m
simulator-68d4c5c4df-zgxv2 1/1 Running 0 6m22s
We can look into pods logs to see that both pods started processing data.
kubectl logs proto-cluster-tutorial-886c9b657-5hgxh
We can do the same experiment as we did for Consul provider and scale down number of replicas to 1 to see that actors are recreated on the node that is still alive.